Introduced by the Indian Government in 2005, the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (NREGA) is a major rural development program. Rural families willing to perform unskilled manual labor will get at least 100 days of wage employment per financial year under the program. Decentralized governance mechanism full with complexity and Gram Panchayats’ crucial role in carrying out NREGA are at the core of it. Delivering NREGA’s promises, influencing grassroots empowerment, and guaranteeing accountability and transparency depend much on Gram Panchayats.
Knowing the NREGA
A demand-driven initiative called NREGA lets rural families seek work rather than passively wait for government provision. Eligible families under the act receive a NREGA job card, which serves as an official record of issued job demands and wages earned. Under NREGA’s rules, this job card is a crucial tool in enabling salary employment and confirming labor records.
Among the goals of the NREGA are:
- Alleviating rural suffering resulting from joblessness.
- Supporting sustainable development through laborintensive projects.
- Reducing wage distribution inequities and promoting social inclusion.
- Preventing job shortages thereby causing rural-urban migration.
Role of Gram Panchayats in NREGA Implementation
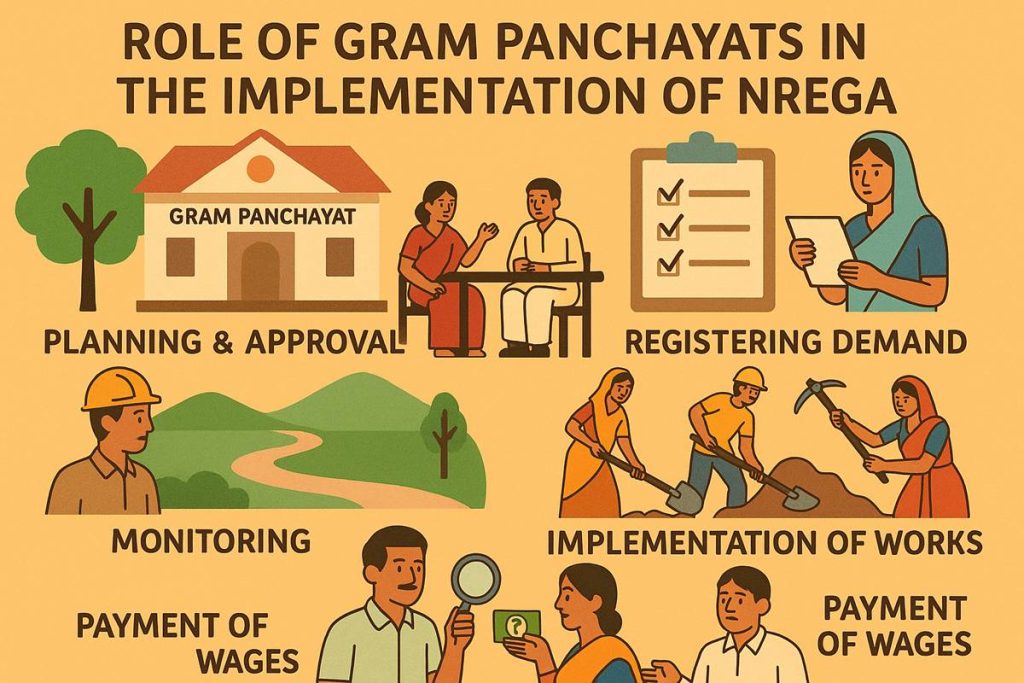
Being the lowest level in India’s rural governance system, gram panchayats bear great accountability in the implementation of NREGA. Their responsibilities include rural employment planning. projects, registering eligible households, issuing NREGA job cards, and monitoring employment activities. Key milestones for Gram Panchayats include:
1. Awareness and Social Action
Among rural areas, gram panchayats are vital for sharing information on NREGA. To educate residents about program advantages and how to get NREGA job cards, Panchayati officials carry out awareness campaigns. Registration helps to guarantee inclusiveness and motivates qualified homes to engage without hesitation.
2. Job Card Registration and issuance
Eligible rural families who want to take advantage of NREGA benefits should register with their local Gram Panchayat. Postverification, the Panchayats issues NREGA employment card. For every cardholder, these cards track employment history, pay received, and length of work done, therefore they have great value. Under NREGA, people cannot legally claim benefits without a job card.
3. Finding Job Prospects
Gram Panchayats work with district-level agencies to find job possibilities fitting for rural workers.
4. Preparing Labor Budgets
Under NREGA, every financial year, each Gram Panchayat is in charge of compiling the labor budget. This requires calculating the expected job needs, workdays, expenses, and resource allocation for execution. For example, if 500 families apply for employment under NREGA inside a Panchayat jurisdiction and the Panchayat calls for the building of water bodies needing 60 workers per day Assuming a daily wage of ₹500 per unskilled worker, Indian Rupees (₹) 54,00,000 would be budgeted for 180 days.
5. Allocation and tracking of wage payments
Under NREGA standards, gram panchayats guarantee that beneficiaries’ compensation is made on schedule. Calculations of wages depend on daily manual labor done and are directly deposited to bank accounts connected to job cards. Payments under NREGA must be made within 15 days following work conclusion. Gram Panchayats also handle complaints regarding wage delays, improper job assignments, and payment discrepancies reported by locals.
6. Guaranteeing Accountability
Transparency is a major feature of NREGA, and Gram Panchayats serve as essential agents in guaranteeing accountability at every stage. Monthly, panchayats hold Rozgar Diwas (Employment Days), where attendance, employment requirements, expenditure, and adherence to program directives are all examined. And wages are openly discussed to stop corruption.
7. Support of Grievance Settlement
Villagers often have problems with late payments, uneven job card distribution, and denial of employment under NREGA. At both block and district levels, Gram Panchayats enable processes of grievance redressal. Leading Panchayat members, a transparent procedure helps to reconcile labor disputes and find redress in cases of discrepancies.
8. Urge Women’s Involvement
NREGA gives gender equality first place by aiming for 33% women participation in its labor force. Gram Panchayats help to engage women for registration in projects. They guarantee that initiatives are intended to meet gender-sensitive roles and salaries free of discrimination.
Difficulties Gram Panchayats Encounter in NREGA Implementation
Gram Panchayats sometimes face obstacles in the implementation of NREGA despite their strong engagement:
- The Panchayat’s limited personnel and expertise cause job card issuance, assignment of labor, and verification of project completions delay and inconsistency.
- Instances of bogus job cards, underreported wages, and ghost postings have tormented the program’s credibility, undermining its integrity.
- Limited job options or projects needing fewer workers than expected demand present difficulties for rural families.
- Resistance from contractors: Certain Panchayats find themselves under pressure from contractors seeking to avoid labor-intensive tasks for profit maximization.
- Promoting gender inclusion, Panchayats occasionally neglect to customize initiatives appropriate for women employees, therefore showing gender bias in execution.
Effect Gram Panchayats Have in Carrying Out NREGA
Gram Panchayats’ active involvement in NREGA implementation has yielded a number of good results:
- Sustainable employment via labor-intensive projects has helped lower India’s rural unemployment rates.
- Under NREGA, efforts have increased public amenities and connectivity in rural communities.
- Empowerment of Women: Increased female participation in work avenues under NREGA has facilitated greater financial and social empowerment among rural women.
- Sustainable income options inside villages have helped the project to effectively curb rural-urban migration.
Disclaimer
Based on publicly accessible data and research insights, this essay offers details on NREGA and Gram Panchayat involvement. Readers should bear in mind that after carrying out proper research and evaluating risks, decisions on public policy investment and Indian financial markets ought only to be made. The author of this piece does not offer expert advice on financial transactions under the above-mentioned plans.
Summary:
Driving rural growth and bridging divides between communities and government initiatives, gram panchayats are vital grassroots agents in the execution of NREGA. Panchayats guarantee clear execution and compliance with program goals from distributing NREGA job card to helping with wage payments and carrying out infrastructure development projects. By including women’s participation in workplace sites, they also tackle labor issues and advance inclusion.
Gram Panchayats have greatly helped to lower rural jobless, upgrade infrastructure, and stop migration despite problems including corruption and bureaucratic ineptitude. Designed for village requirements, sustainable employment programs have better the financial situation of millions of people throughout India. Still, to completely unleash the power of NREGA, structural problems call for changes.